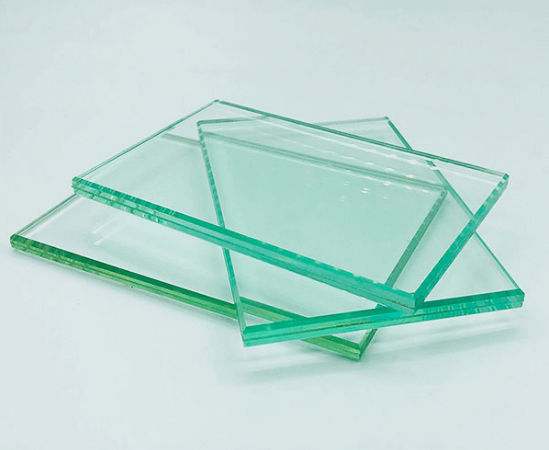
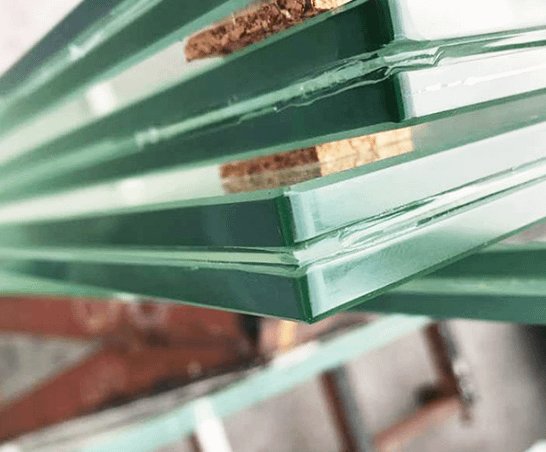
A type of safety glass that is made by sandwiching a layer of plastic (PVB or polyvinyl butyral) between two layers of glass. This process, known as interlayering, creates a strong and durable glass that can help prevent shattering and provides additional protection against external forces. The PVB interlayer absorbs the energy of an impact, helping to prevent the glass from shattering into sharp pieces.
Where it is used:
Laminated glass is widely used in various applications where safety and security are critical. Some common examples include:
- Automotive industry: Laminated glass is used in side windows, rear windows, and windshields of vehicles due to its ability to prevent shattering and reduce the risk of injury.
- Security applications: Laminated glass is used in secure areas such as government buildings, banks, and high-security facilities due to its ability to prevent breakage and penetration.
- Architectural glass: Laminated glass is used in building facades, windows, and doors due to its ability to provide sound insulation, reduce noise pollution, and prevent shattering.
- Aviation industry: Laminated glass is used in aircraft windows and doors due to its ability to withstand high-pressure differences and extreme temperatures.
- Railway industry: Laminated glass is used in train windows and doors due to its ability to withstand vibration and extreme temperatures.
- Home and office applications: Laminated glass is used in furniture such as coffee tables, shelves, and desks due to its durability and scratch-resistance.
- Skylights and greenhouses: Laminated glass is used in skylights and greenhouses due to its ability to provide UV protection and prevent shattering.
Overall, laminated glass is an essential material in various industries where safety, security, and durability are paramount.